Bayesian Approaches For Modeling Protein Biophysics
Keegan Hines
Aldrich Lab
Outline
Background
Parameter Identifiability in Nonlinear Biophysical Models
Modeling Single Molecule Time Series Using Nonparametric Bayesian Inference
Proteins
- Fundamental unit of computation and signal processing in biological systems
- Fold into complex structures which determine their function
Proteins
- Proteins are dynamic, exploring very many conformational states.
- What can we do to understand these dynamics?
Jensen et al., 2012, Mechanism of Voltage Gating in Potassium Channels, Science , 336, 6078.
Modeling Proteins
Physiological relevance- we only need to account for some of this complexity
Modeling Natural Systems
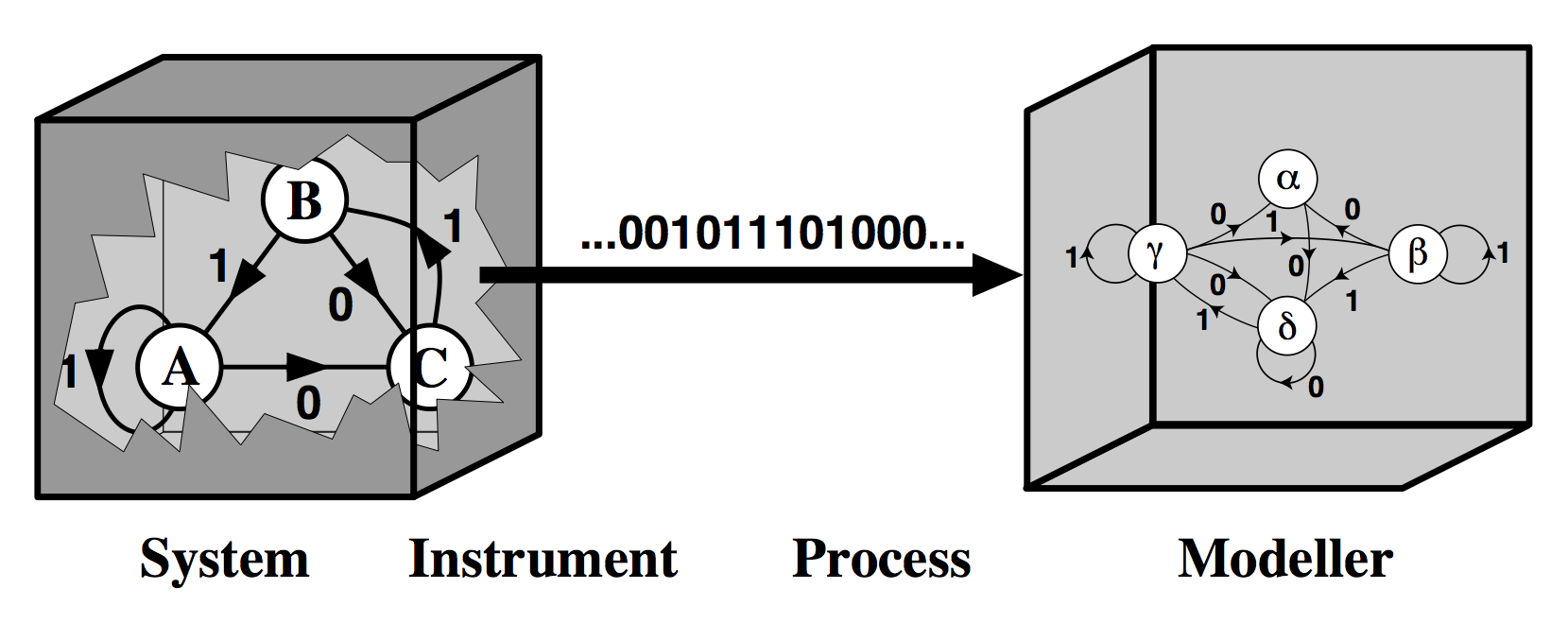
Imagery stolen from Jim Crutchfield lecture notes
Parameter Identifiability in Nonlinear Biophysical Models
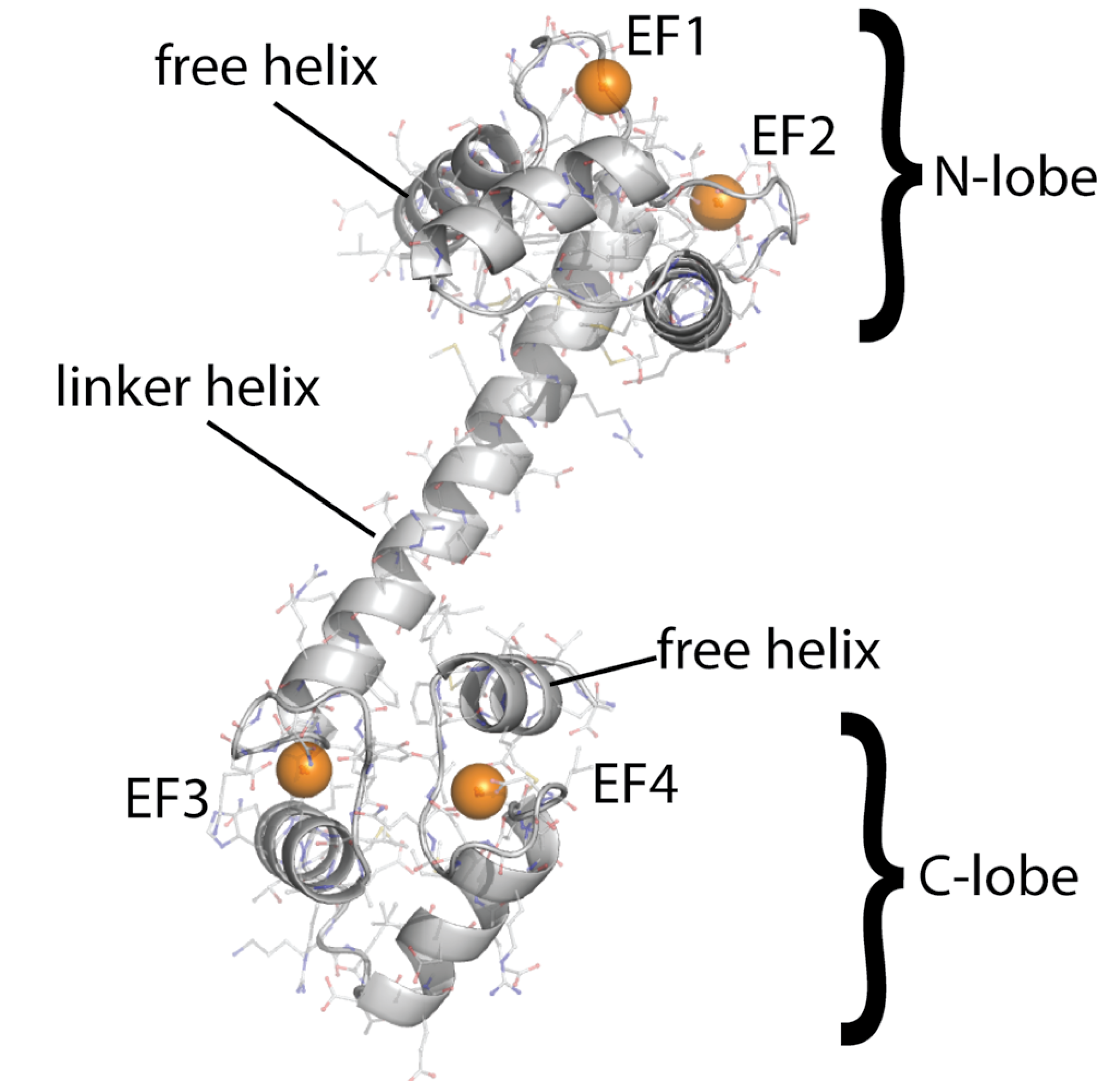
Calmodulin
Calmodulin
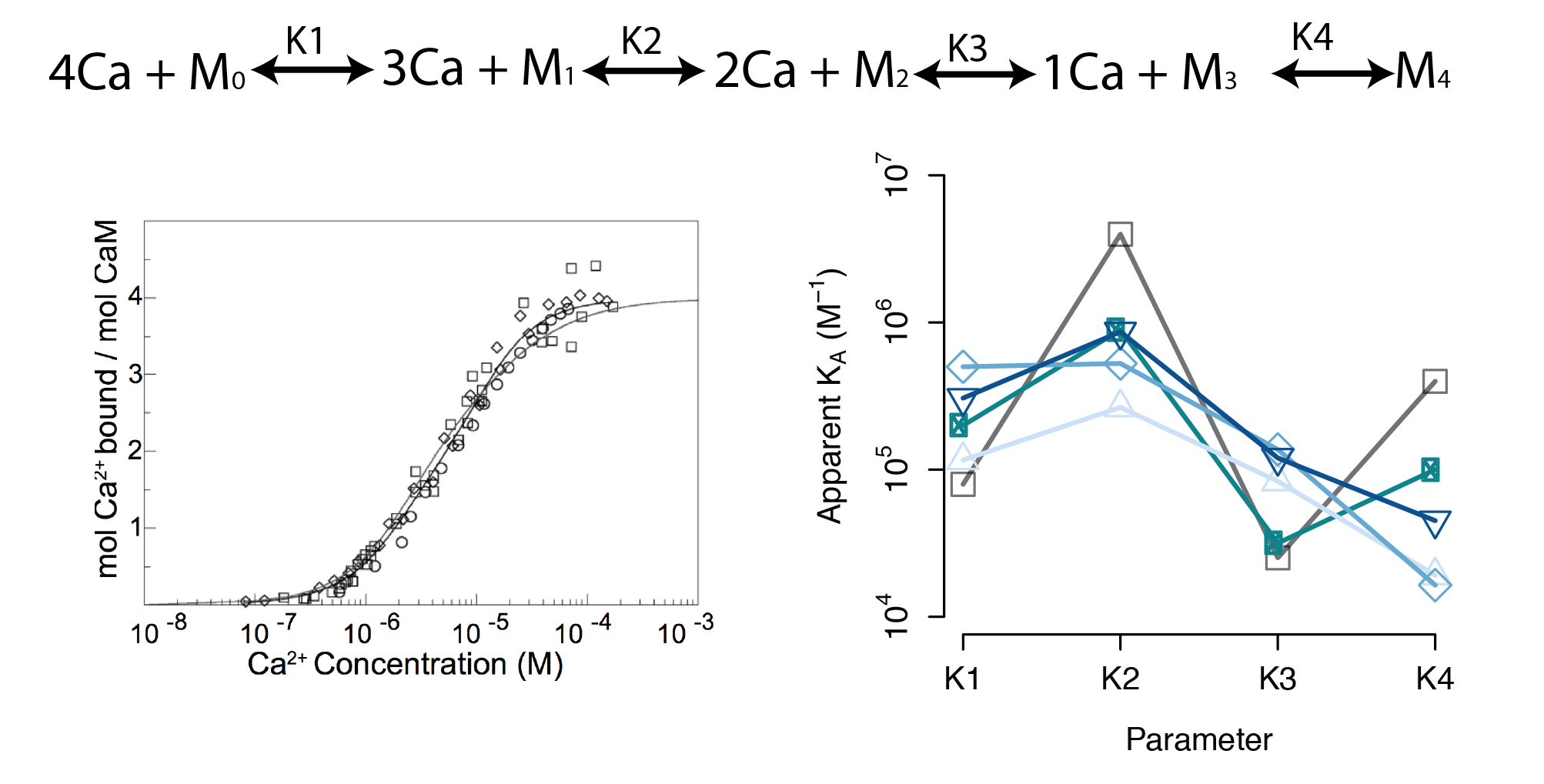
- A sequential binding model is often used to study CaM
- Current estimates of binding parameters vary wildly
Stefan et al, 2009. Computing phenomenologic Adair-Klotz constants from microscopic MWC parameters. BMC Systems Biology. 3:68.
Sequential Binding Model
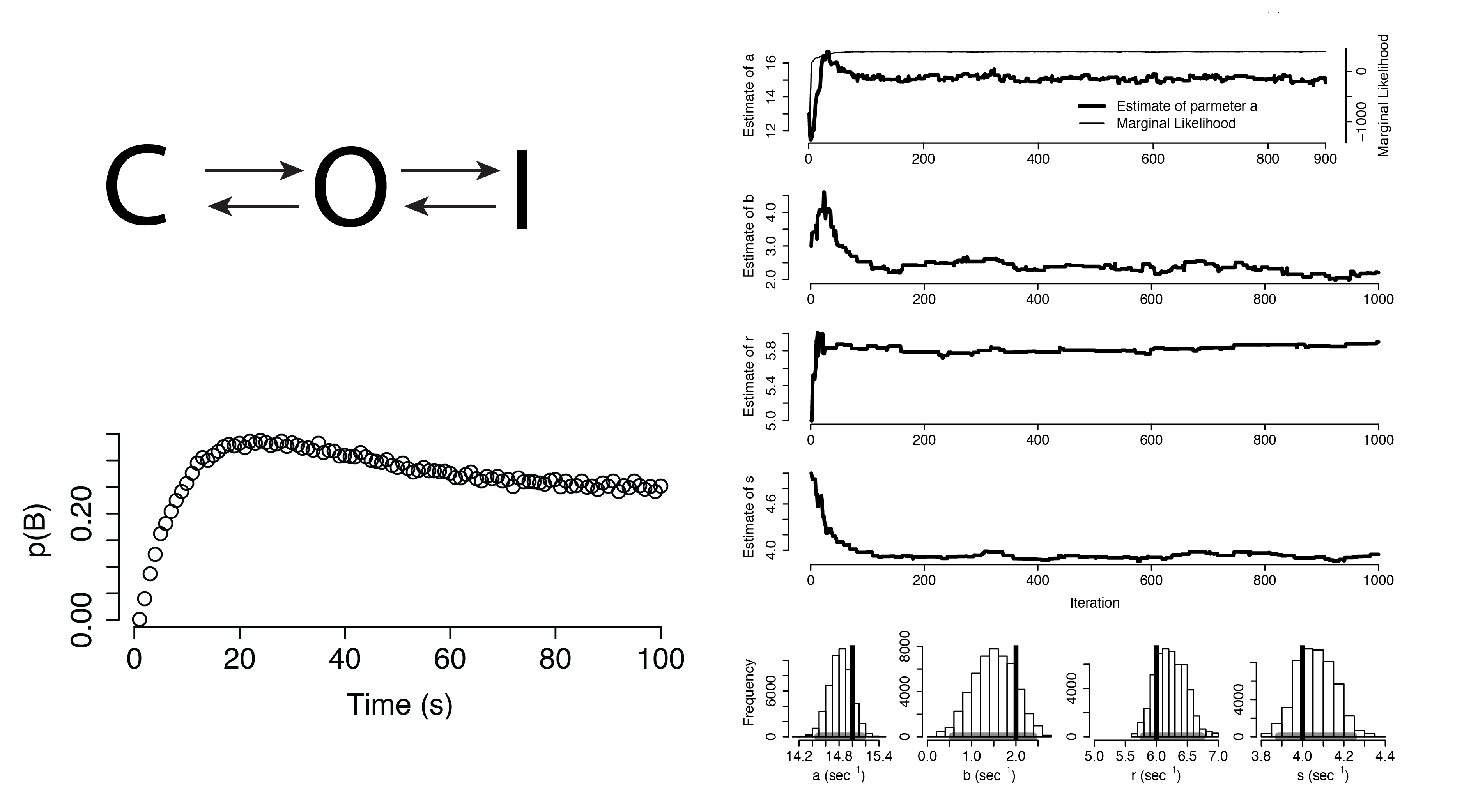
Large regions of this parameter space can fit any data extremely well
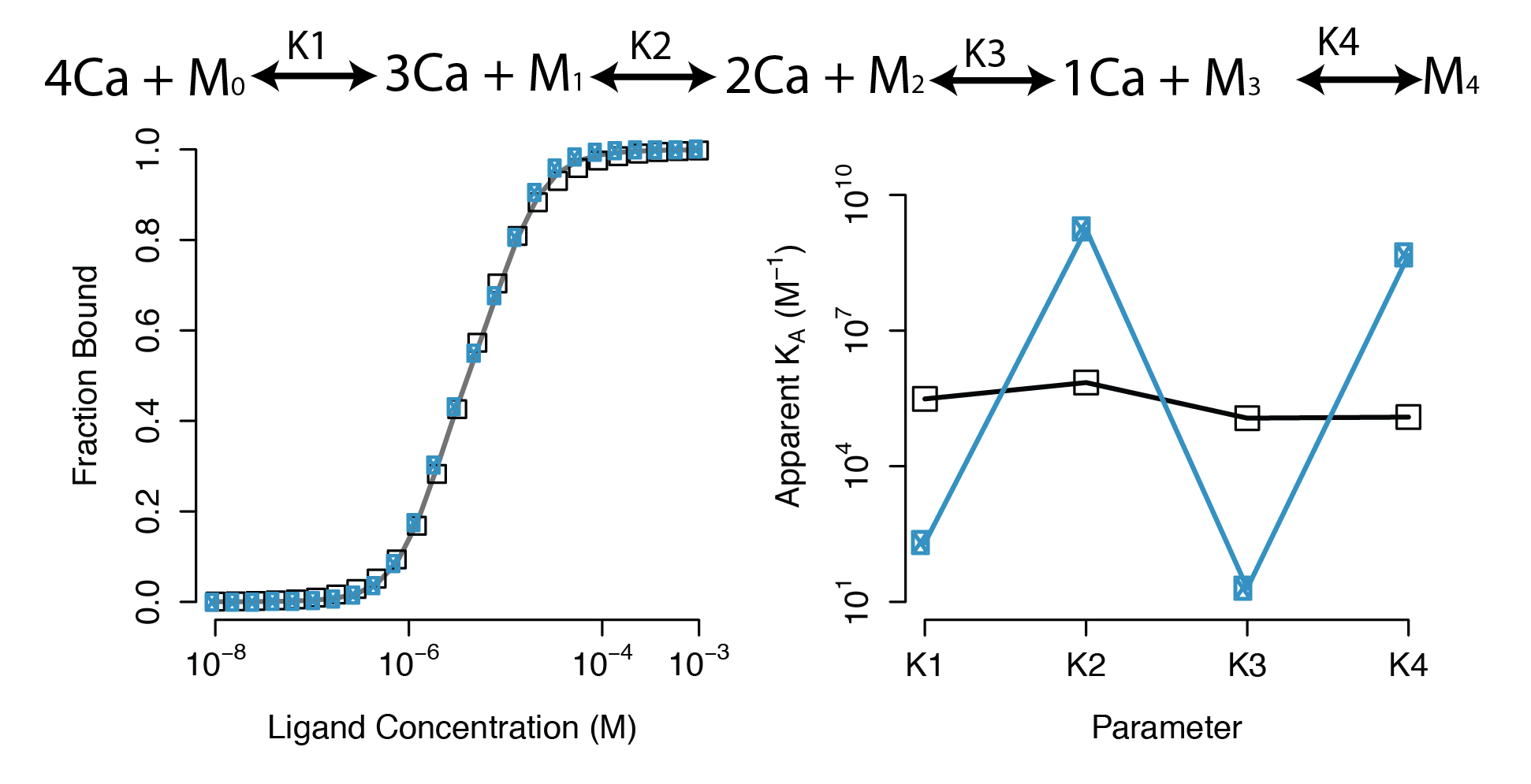
Parameter Identifiability
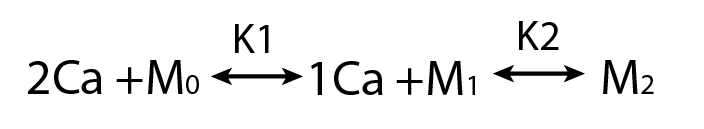
Parameter Identifiability
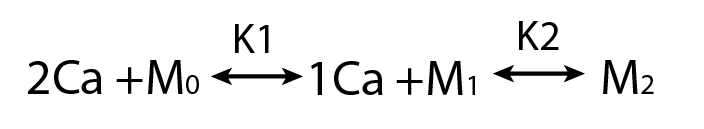
Practical Non-identifiability
Structural Non-identifiability
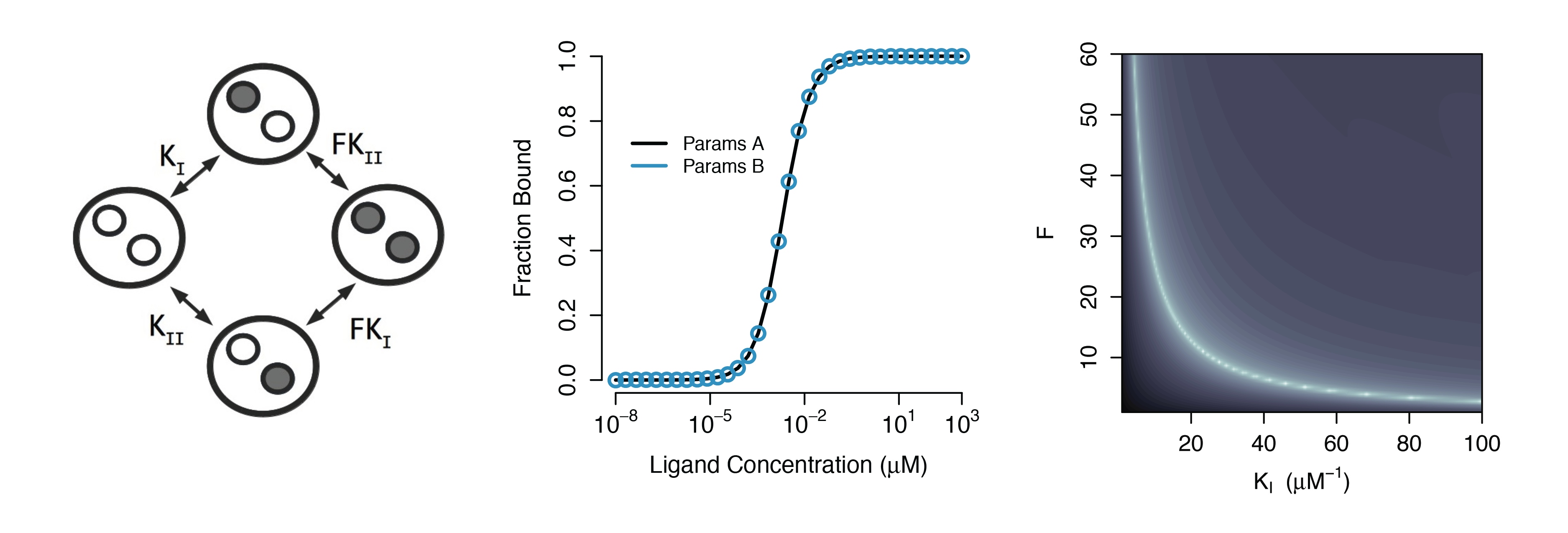
Parameters cannot be inferred accurately even with noiseless data
Identifying Identifiability
Analytical methods exist, but can only be used in special cases. Worse, such methods can be misleading, as in the case of practical non-identifiability.
We might calculate the Error (likelihood) over the whole parameter space, but this is infeasible for many parameters.
We need an efficent way to identify the regions of parameter space that lead to good agreement with the data.
Bayesian Inference
The posterior distribution quantifies which regions of the parameter space provide a good explanation of the data.
Bayes' rule specifies how to calculate posterior probability, and Markov chain Monte Carlo provides an efficient method to estimate high-dimensional posterior distributions.
Markov chain Monte Carlo
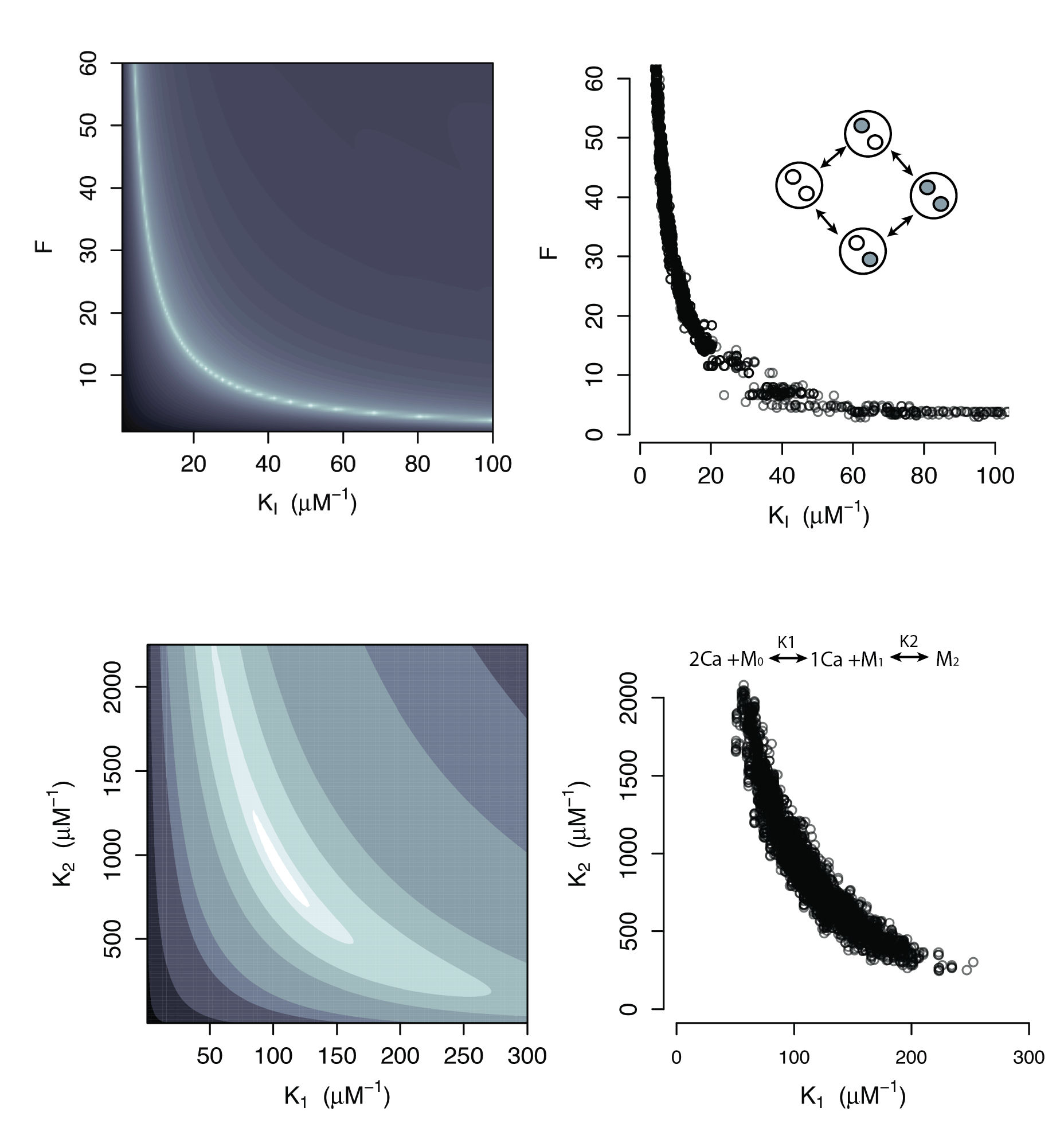
Additional Applications
Dynamical Systems
Additional Applications
Dynamical Systems
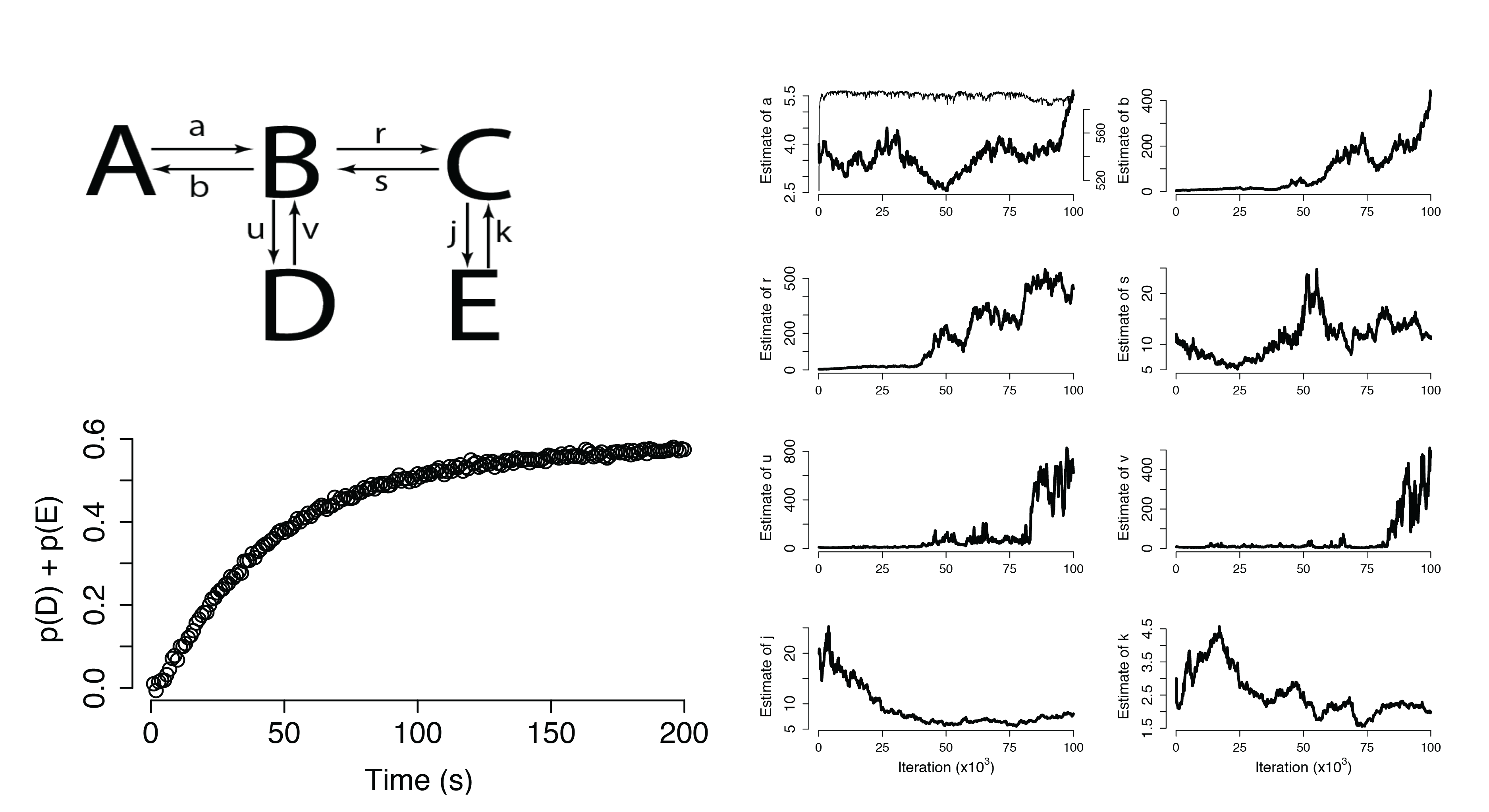
Additional Applications
Dynamical Systems
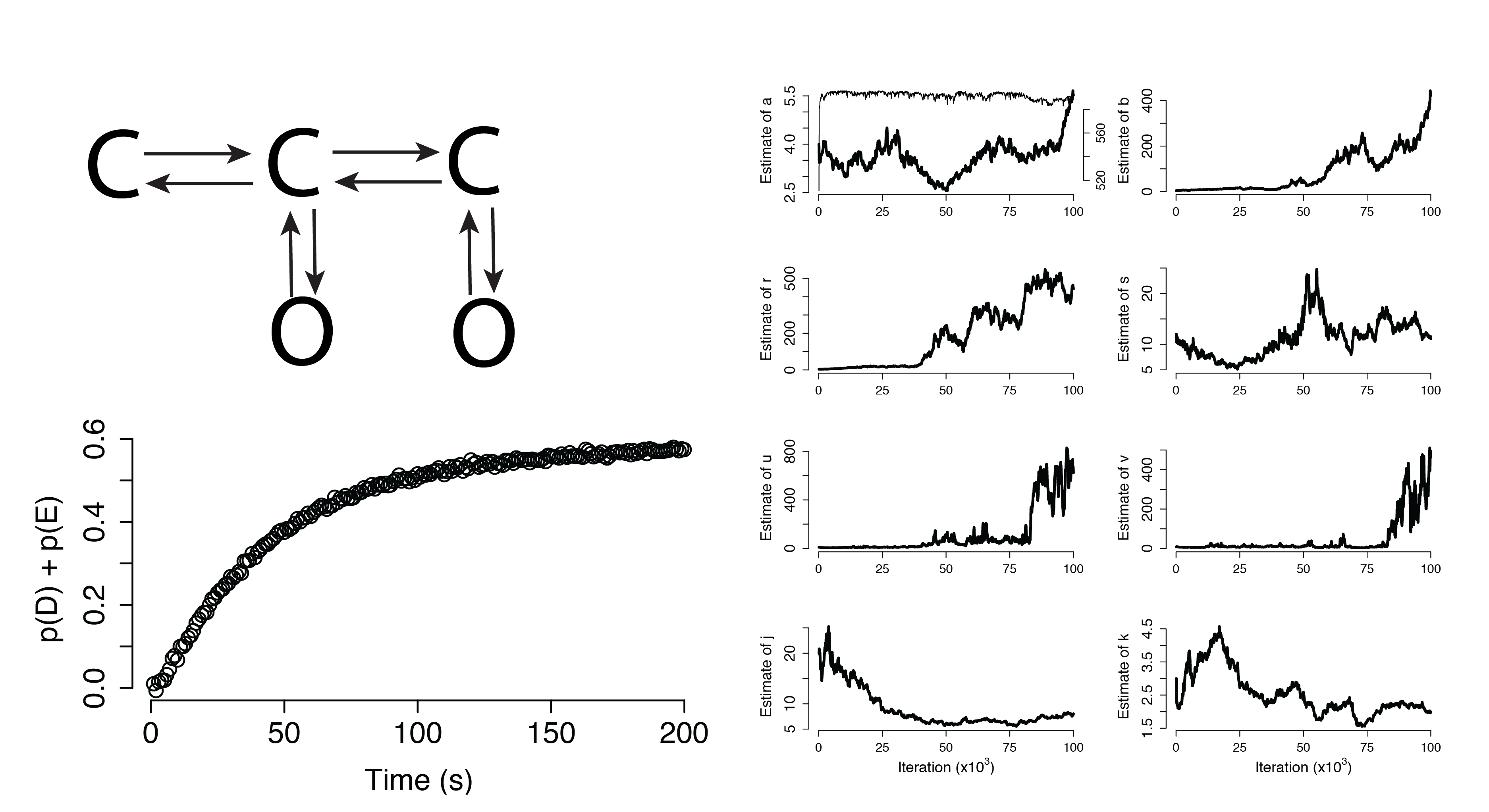
Additional Applications
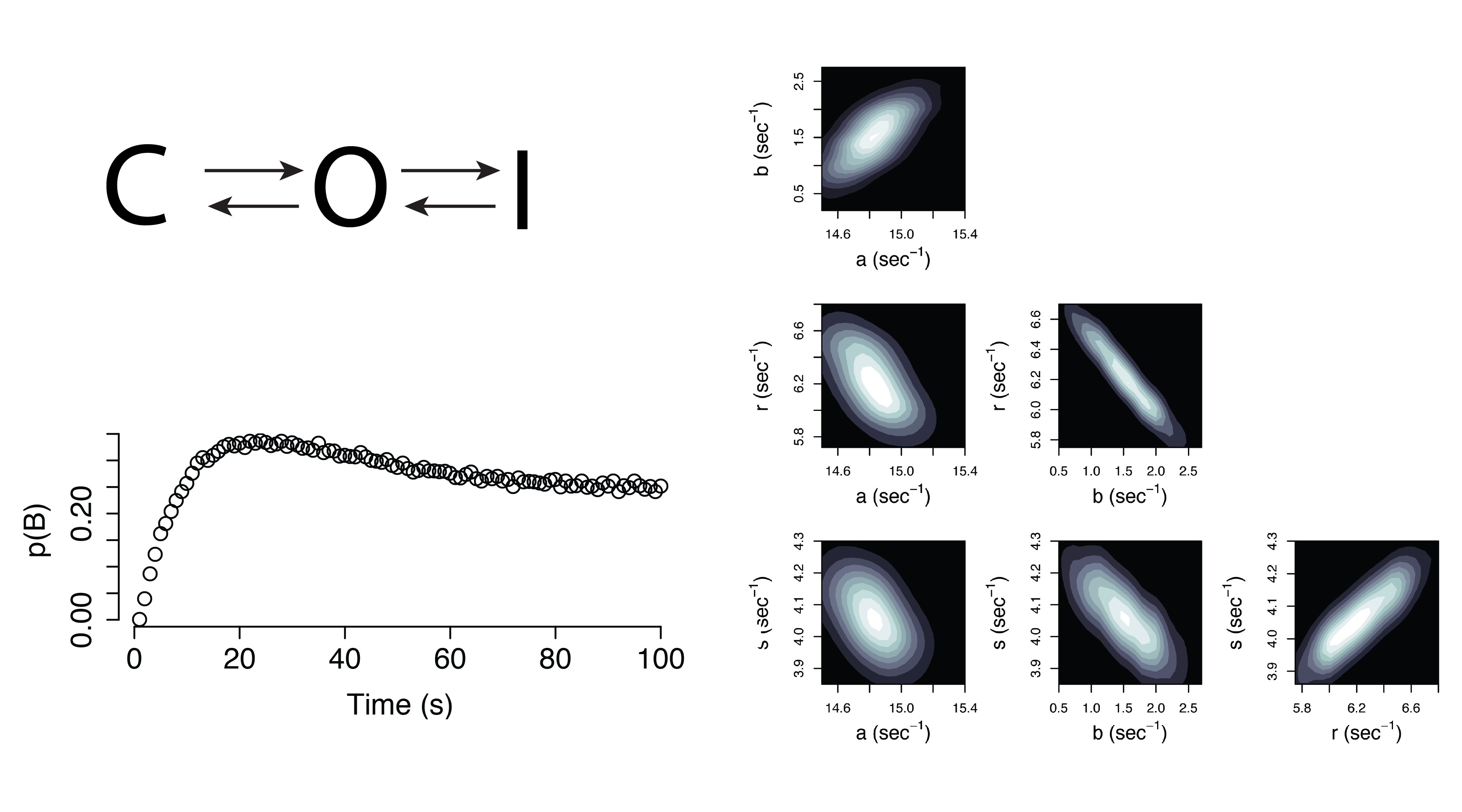
Dynamical Systems (Non-Identifiable)
Additional Applications
Dynamical Systems (Non-Identifiable)
Model Selection and Experimental Design
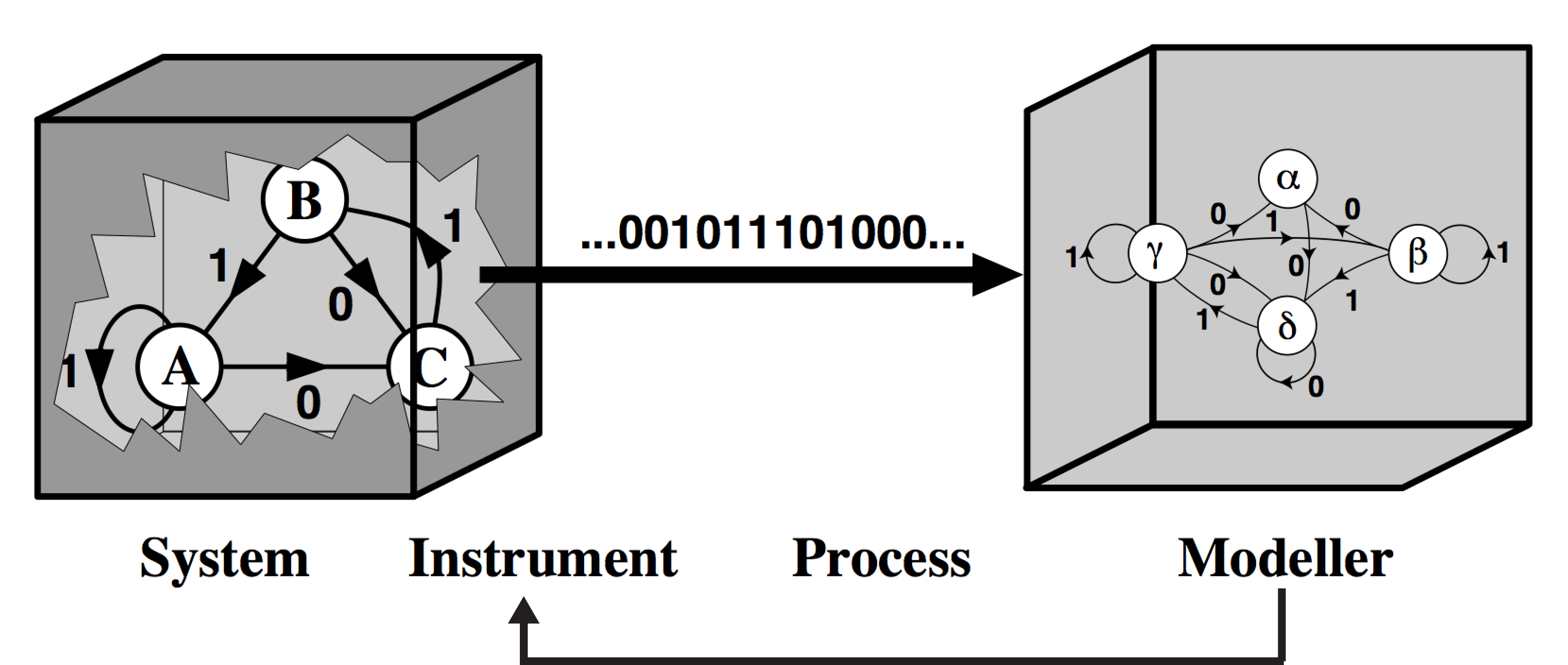
Modeling now becomes an iterative process, where non-identifiability forces innovative experimentation
Model Selection and Experimental Design
Conclusions
- Mechanistic models of proteins systems are important, though merely fitting data to models is insufficient: fits may not be unique
- Non-identifiability is a concern not only for large and complex models, but also for extremely simple 2- and 3-parameter biophysical systems
- New methods are required to determine the accuracy and identifiabilty of nonlinear models
- Bayesian inference (& MCMC) is well suited to provide accurate parameter estimates and a direct assessment of identifiability
- This approach will yield more accurate modeling and will force more innovative experimentation
Modeling Single Molecule Time Series Using Nonparametric Bayesian Inference
Single Molecule Measurements
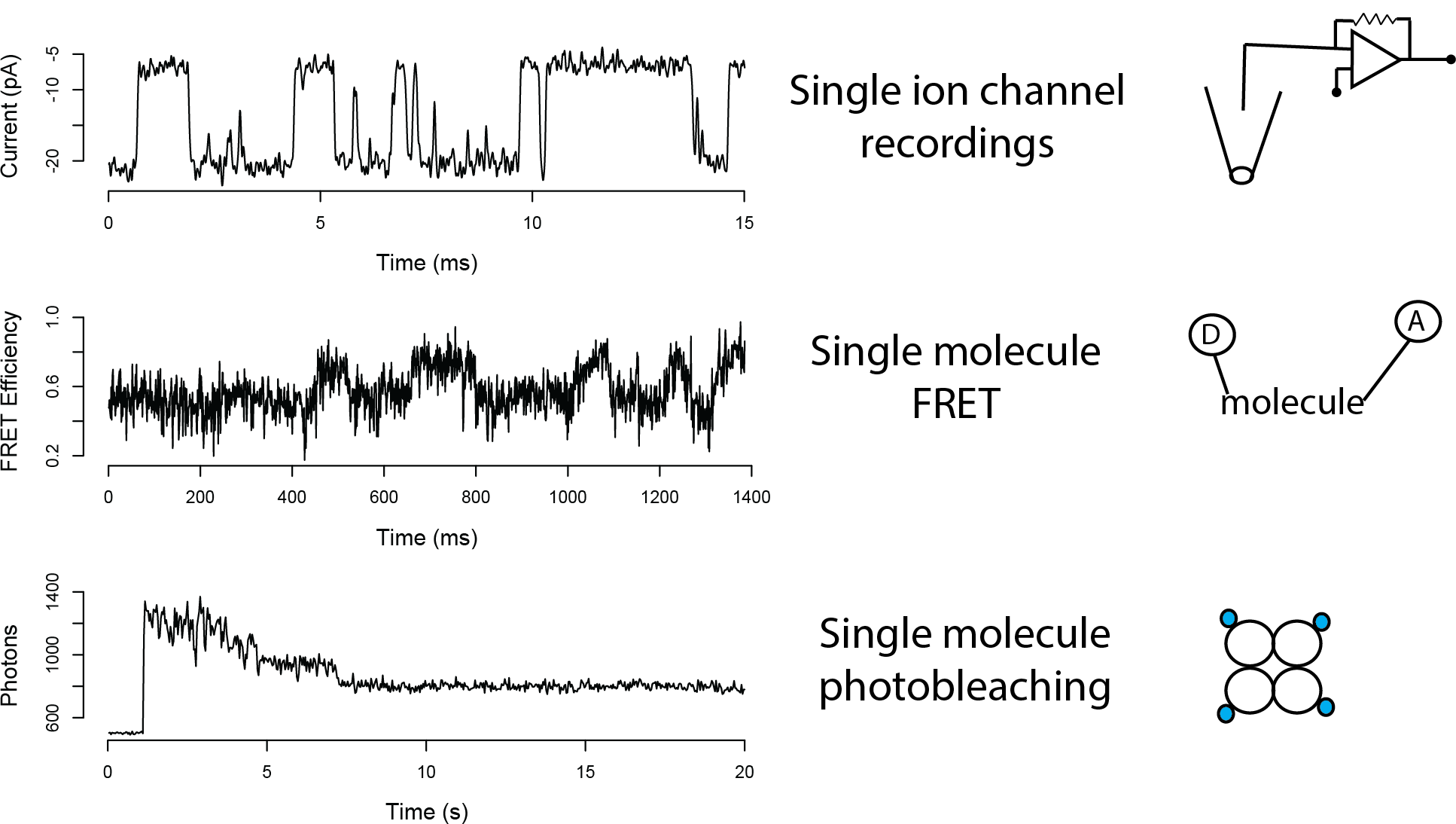
Modeling Single Molecule Time Series
Modeling Single Molecule Time Series
Nonparametric Bayes
Rely on a flexible class of infinite dimensional probability distributions - the Dirichlet process
We can extract structure from data, instead of assuming models beforehand
Structure might refer to hidden closed and open states in single channel recordings, or to conformational states in FRET traces, or to bleaching events in photobleaching traces
Dirichlet Process
Provides an infinite dimensional probability distribution
But has useful clustering properties when modeling finite data
Stick Breaking Process
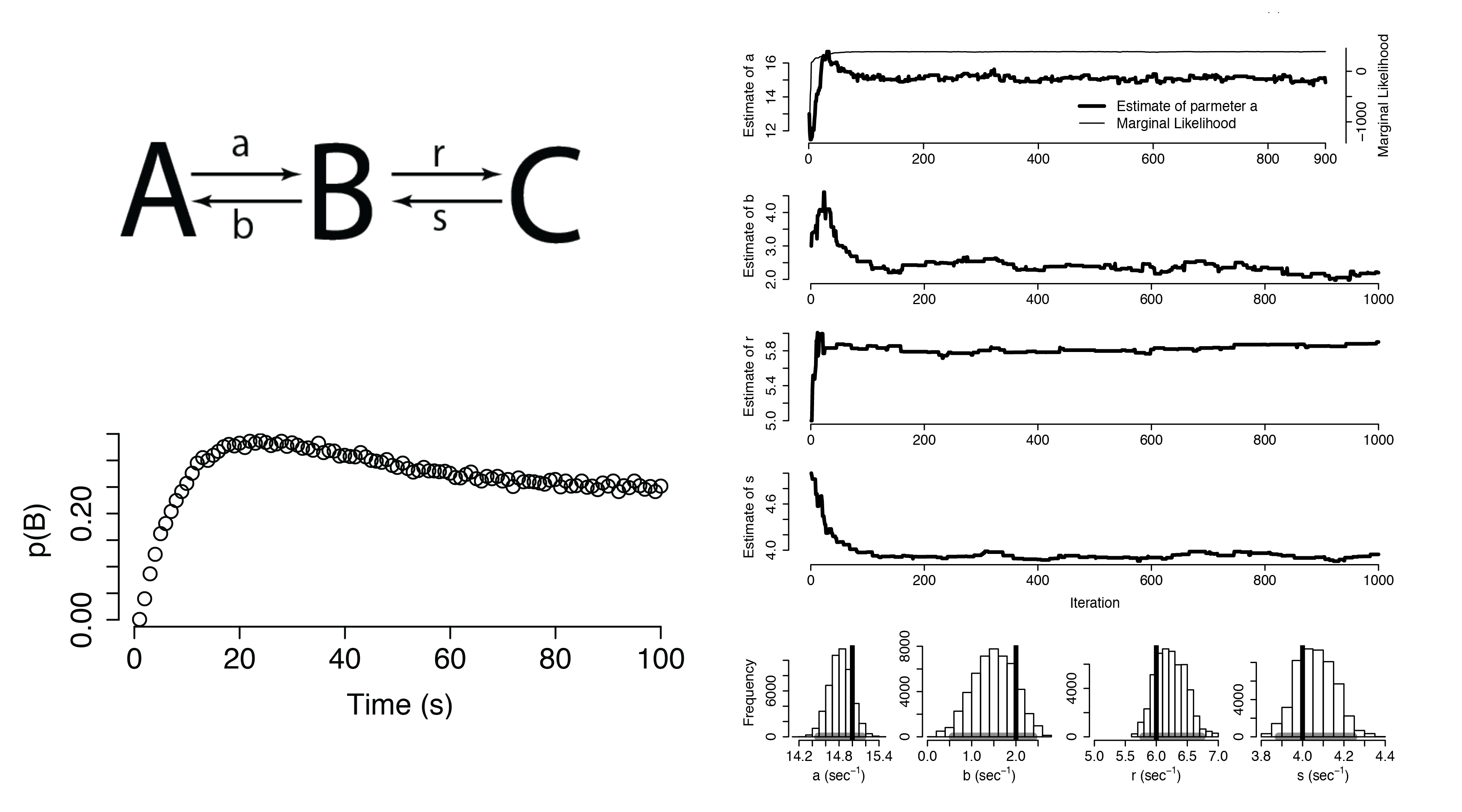
Hidden Markov Models
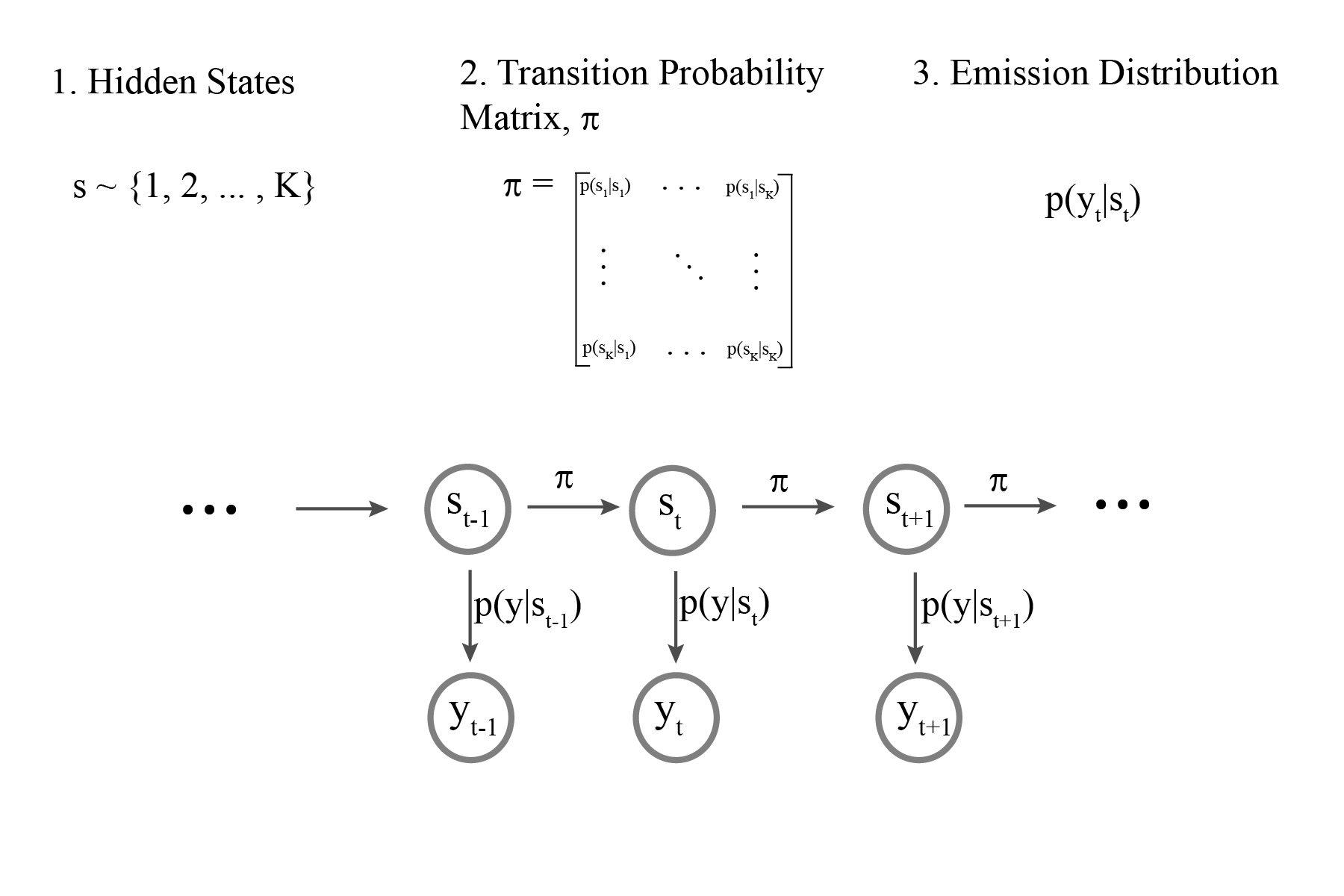
Hidden Markov Models
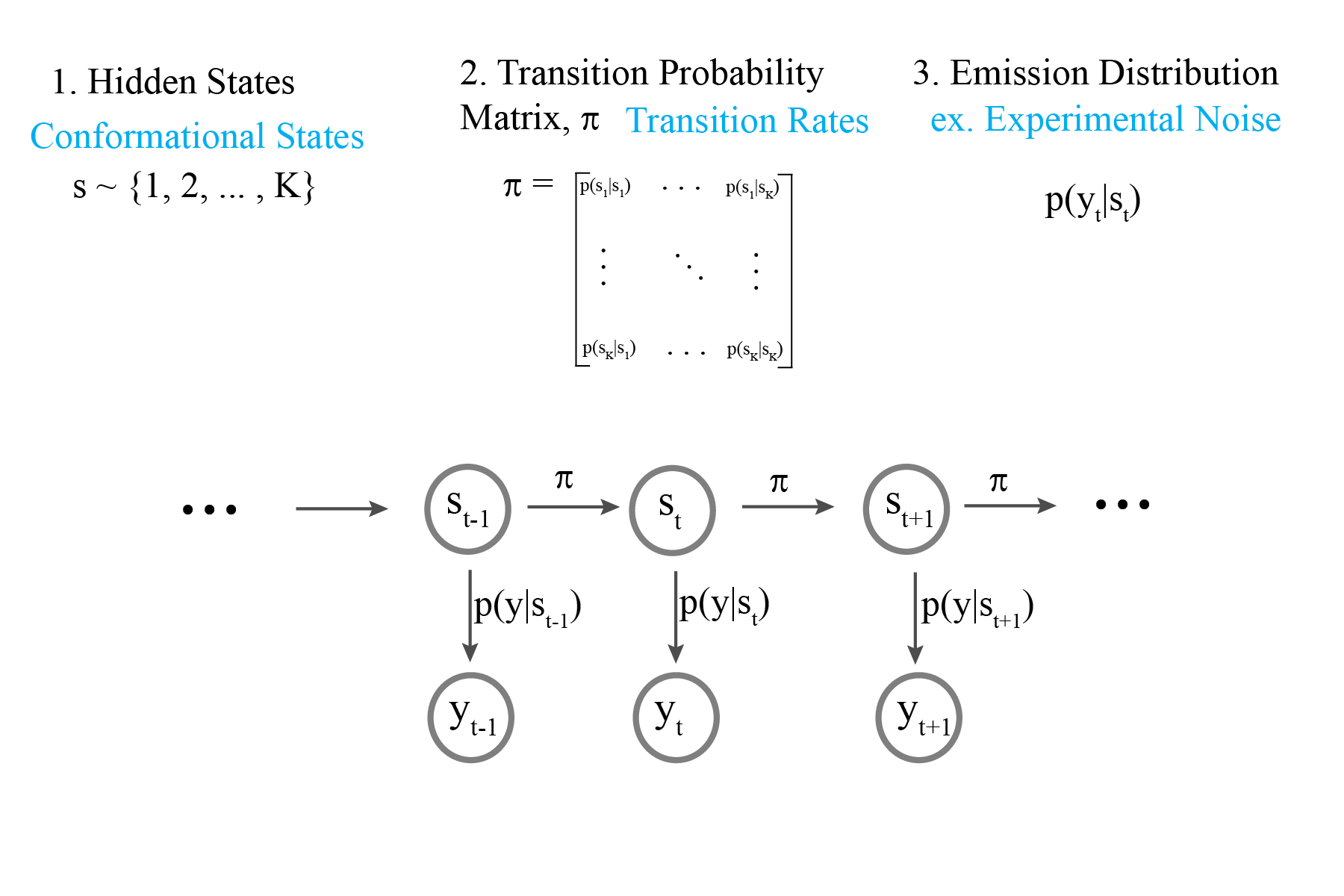
Infinite Hidden Markov Model
We now model the transition matrix as the bi-infinite Hierarchical Dirichlet Process
Our model now specifies transitions to and from an infinite number of hidden states
Using this infinite model allows us to discover the number of hidden states in a time series
Infinite Hidden Markov Model
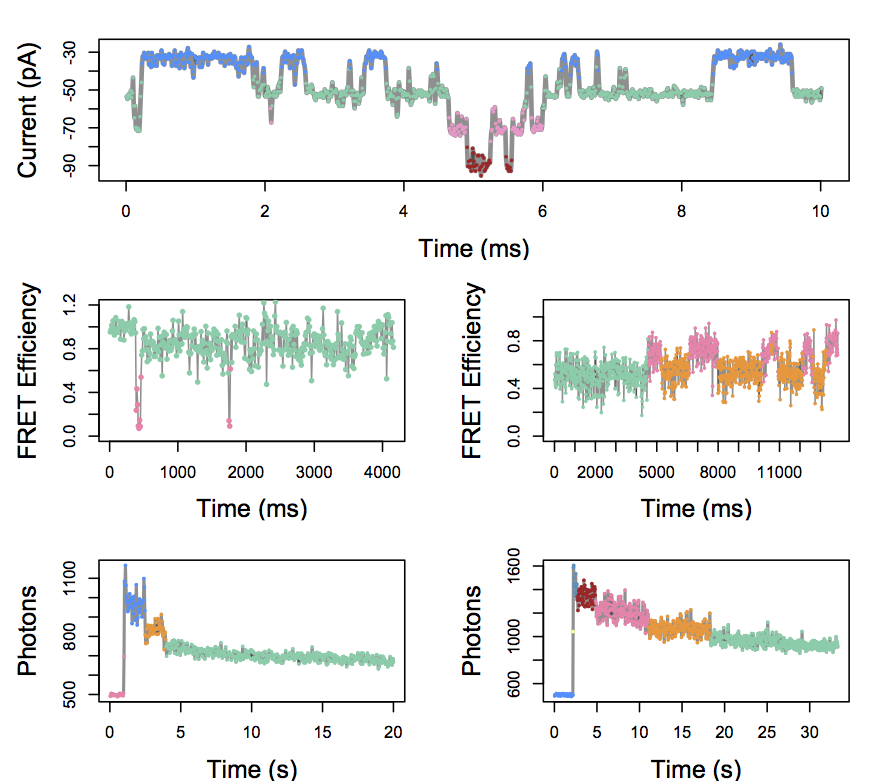
In each of these cases, we can detect the presence of distinct hidden states.
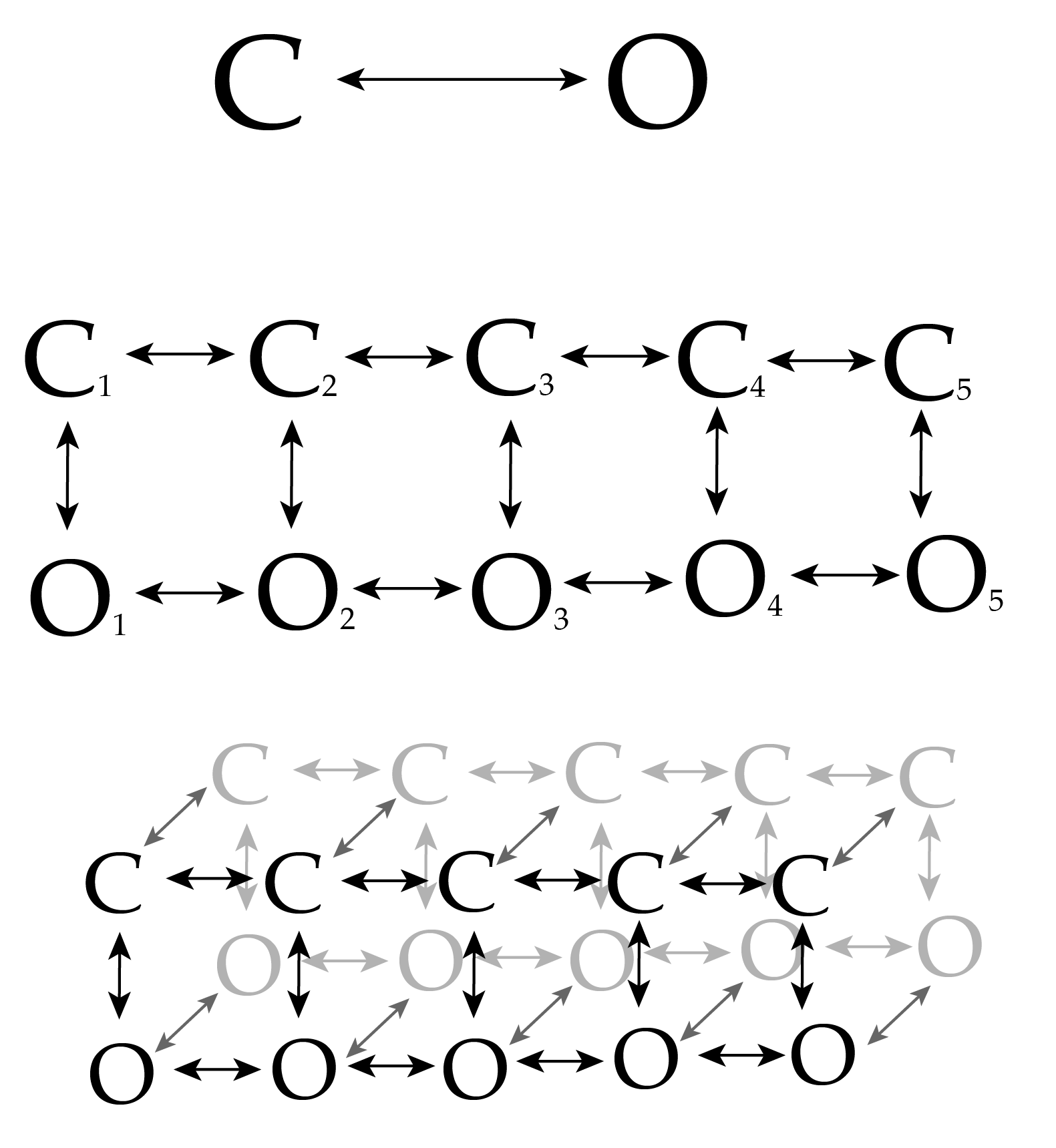
Aggregated Markov Model
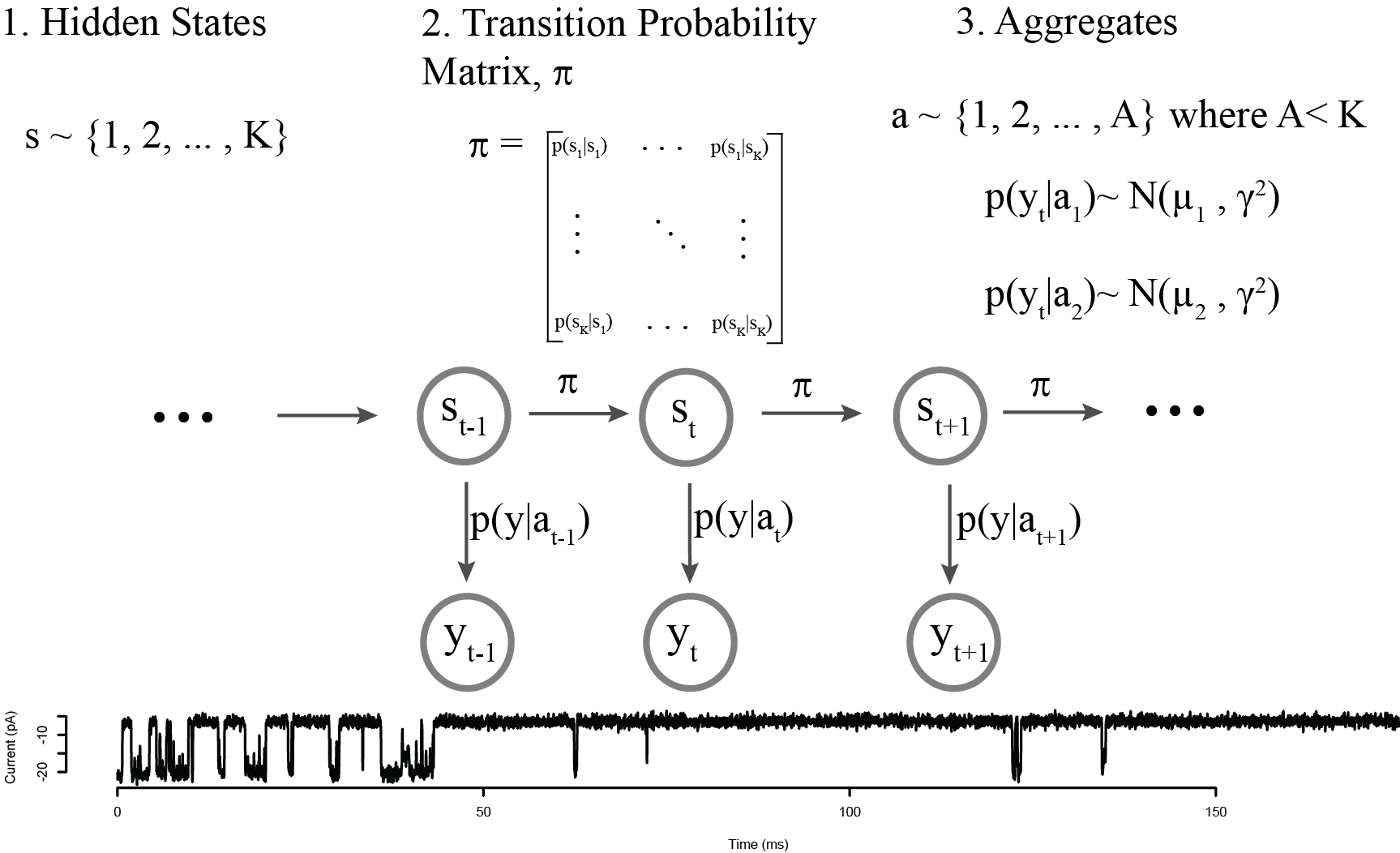
Infinite Aggregated Markov Model
We think there's only two conductance states (open and closed), but an unknown number of hidden states
Again, we now model the transition matrix as the bi-infinite Hierarchical Dirichlet Process
Our model now specifies transitions to and from an infinite number of hidden states, each of which appears as either open or closed
Using this infinite model allows us to discover the number of hidden states in single channel recording
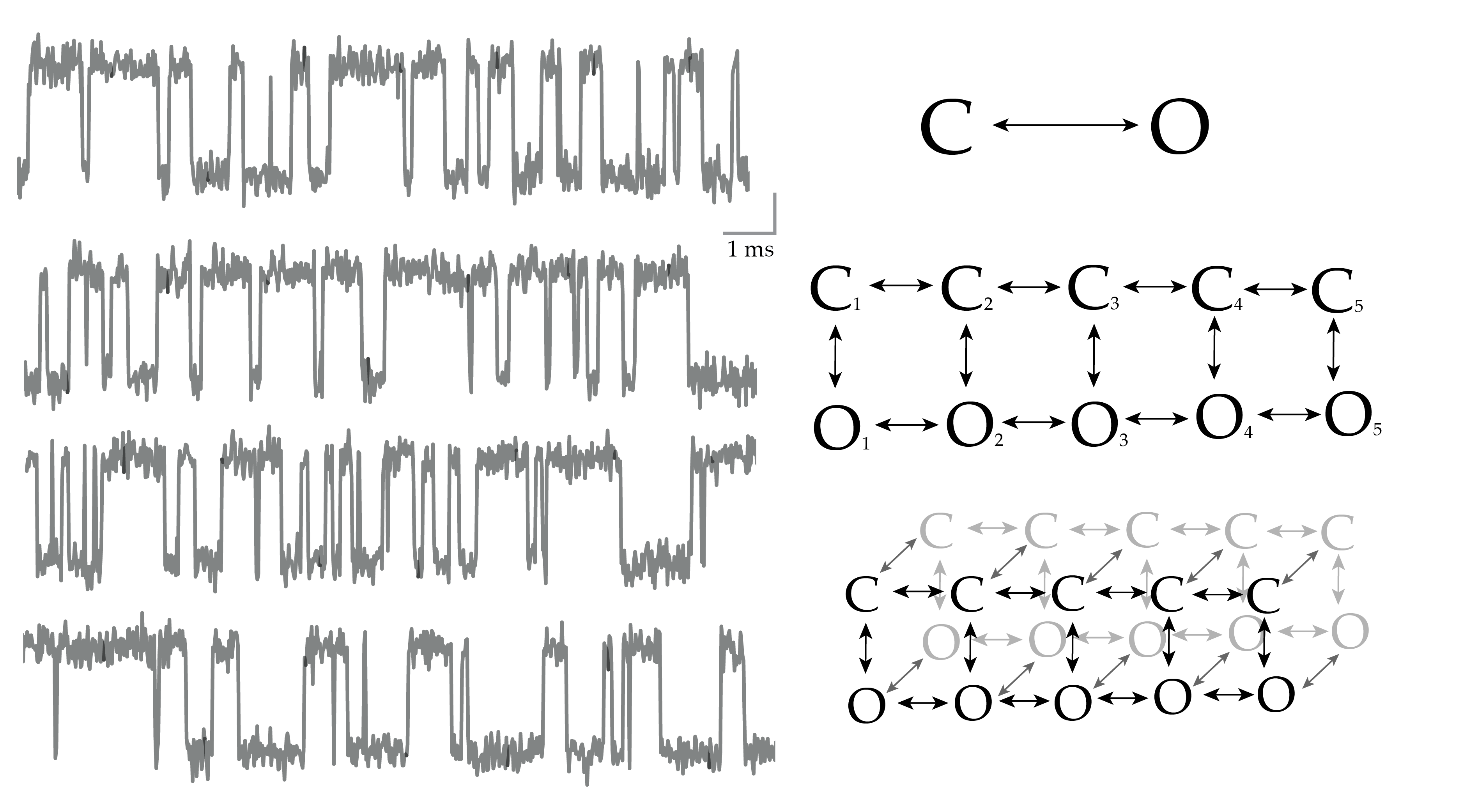
Infinite Aggregated Markov Model
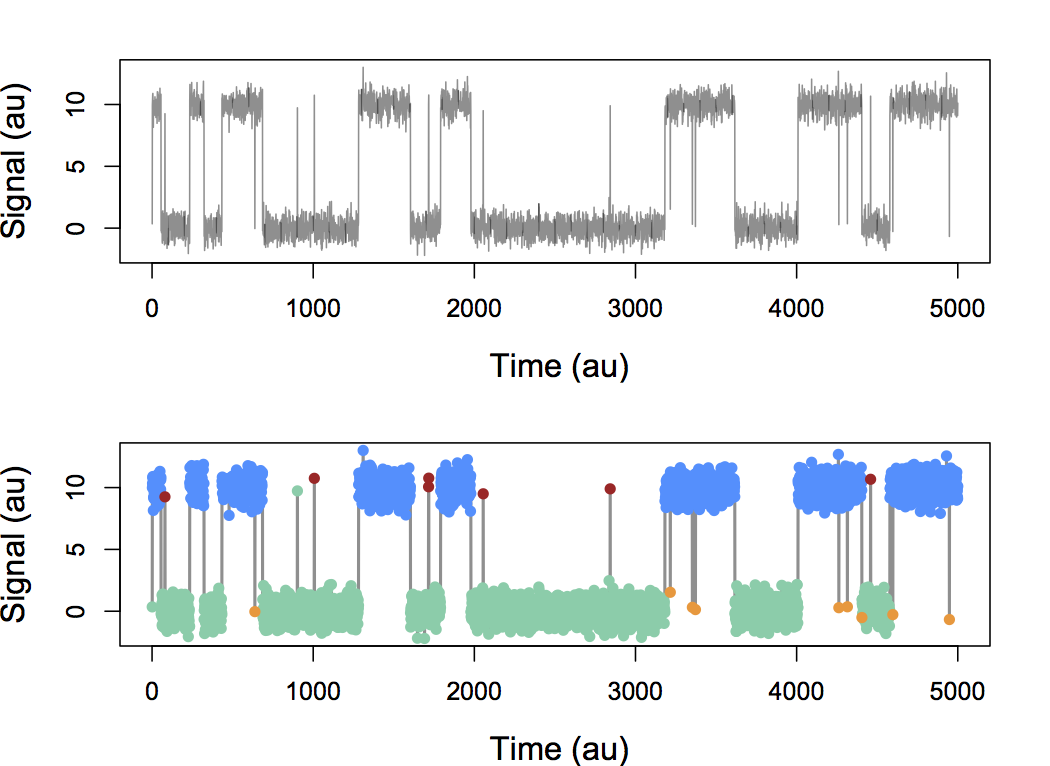
With simulated data, we can indeed discover hidden states based only on their different dynamics
Infinite Aggregated Markov Model
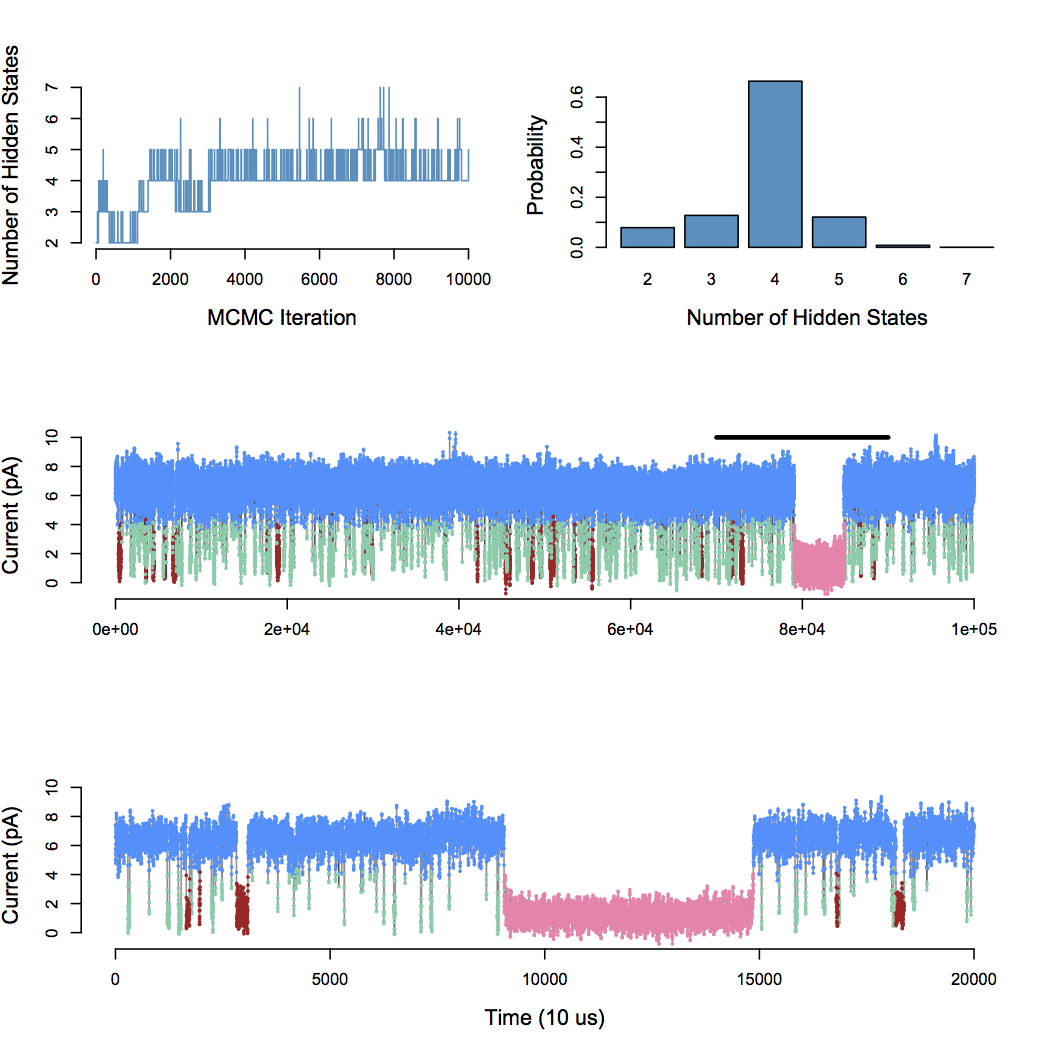
Application to BK channel data
Infinite Aggregated Markov Model
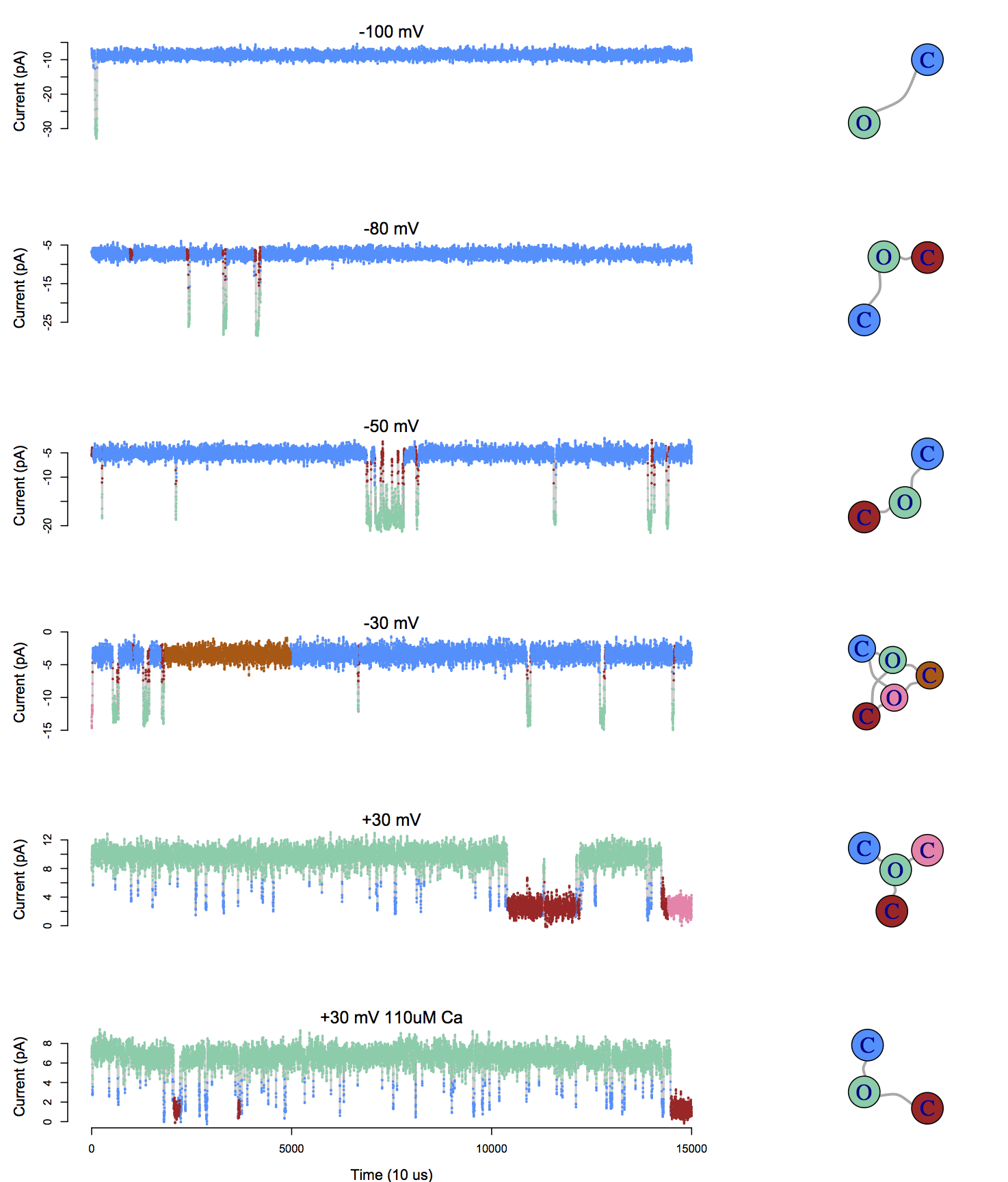
Nonparametric Bayes approach uncovers the complexity of channel gating
Conclusions
- Powerful experimental methods allow us to measure the properties of proteins at the single molecule level
- Developing rigorous and general tools for the analysis of such data remains an open challenge
- Nonparametric Bayes methods can be used to discover structure in data instead of assuming models
- These methods were demonstrated with diverse data sets including single channel recordings, single molecule FRET and single molecule photobleaching
Acknowledgements